REvil Ransomware Threat Research Update and Detections

On July 2, 2021, rumors of a "supply-chain ransomware" attack began circulating on Reddit and was later confirmed by Kaseya VSA, a remote monitoring management software. Kaseya shared in an open statement that this cyber attack was carried out by a ransomware criminal group called REvil, where they used Kaseya to distribute ransomware to its on-premises customers. On July 5, 2021, our team at Splunk pushed out a rapid response blog to help organizations detect REvil Ransomware Kaseya in Splunk. While Splunk was not impacted by the ransomware attack, as a security leader we want to help the industry by providing tools, guidance and support.
Today, we’re here to provide more insights and research around this ransomware organization, in hopes to help businesses around the world understand the group and their tactics.
Introduction to REvil
The REvil payload (Ransomware Evil or also known as Sodinokibi) is ransomware as a service criminal enterprise. REvil is said to be related to the criminal group known as GandCrab. In a Ransomware as a service scheme, malicious actors partner with affiliates to extend their botnets and reap profits from new additions and attacks brought to them by affiliates. The profit is shared with affiliates which encourages them to infect more victims.
The REvil payload is associated with some of the following attack vectors:
- Elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) for file encryption (files, shares)
- Windows Remote Desktop (RDP) brute force entry
- Double extortion threat
- Target VPN devices
- Phishing emails
- Affiliates may choose different attack vectors including specific software exploitation
Understanding How REvil Ransomware is Executed in a Simulation
The following images show REvil ransomware execution replicated via Splunk Attack Range. First, we can see the ransom note indicating the site located on the dark web where the victim needs to go for further information.

The ransomware payload does not disable the systems completely, even though the documents are indeed encrypted, the system is left with enough capacity to download the TOR browser program and install it. Once a victim browses to the named site via TOR browser, they find a form where the key found in the ransom note is meant to be entered. Notice there is a captcha in this form.

After entering the key the victim is presented with a page with instructions on the steps to follow to be able to decrypt the files.

In the following capture, the Monero (XMR) address where victims are supposed to send payment can be seen.

The next capture shows the Dark Web page where the REvil ransomware gang advertises the information they claim they obtained from victims that did not pay the ransom.

REvil Command-line Arguments
REvil Ransomware also has several command line parameters to dictate its behavior or features it wants to execute.

Command-line Parameter | Description |
-nolan | Do not encrypt network share |
-nolocal | Do not encrypt the local drive |
-path | Encrypt specific folder path |
-fast | Fast encryption |
-full | Encrypt both network and local drive |
REvil Configuration JSON File
REvil uses RC4 encryption/decryption algorithm to decrypt its notable strings and its configuration file. REvil does this by parsing the 0x20 bytes RC4 key placed in one of its sections and verifying the checksum hash of the encrypted config file in its code body. This configuration file (JSON format) contains information and conditions on how it will encrypt the files in the compromised machine.
Below is the screenshot and description of the notable field in that configuration file.


REvil Config Field Name | Description |
pk | Public key (in Base64) |
pid | REvil versioning ID |
sub | REvil tag number |
dbg | Is it dbg mode |
wipe | Wipe folder flag |
fld | folder list it wants to skip during the encryption process |
fls | File list it wants to skip during the encryption process |
ext | File extension it wants to skip during the encryption process |
wfld | The folder it wants to wipe |
prc | Process name list it wants to terminate |
dmn | REvil C2 domain list |
svc | Service name list it wants to stop |
nbody | Ransomware notes in base64 format |
nname | Ransomware notes file extension |
img | Ransomware notes that will be in bitmap form |
arn | Persistence flag |
net | C2 communication flag |
Kill Switch for REvil Ransomware
This ransomware also has a kill switch. It tries to avoid compromising a machine with a specific keyboard layout and languages like (Russian, Ukrainian, Belarusian, and many more) as shown in the screenshot below.

Privilege Escalation
REvil Ransomware will try to run itself using “runas” command to have a privilege escalation of execution.

Persistence
If the “arn” field in its configuration file is enabled, it will create an autorun registry on the compromised machine as a persistence mechanism.

Defacement
Aside from the ransomware notes, it will generate in several folders in the compromised machine, it will also create a bitmap containing a note that the machine is also infected.

COM Object
The Splunk Threat Research team also found some function in REvil ransomware where it uses com object IWbemClassObject “4590f811-1d3a-11d0-891f-00aa004b2e24” and “49BD2028-1523-11D1-AD79-00C04FD8FDFF” to execute root/cimv2 namespace or privilege escalation.

Other Registry Entry
REvil is known to have a randomly generated file extension (5-10 characters) that will be used for its ransomware notes filename and for the files it encrypts. This randomly generated string will also save in a unique registry key. In this case, the randomly generated file extension is “.teu459110”

Machine Info
REvil ransomware will also gather some information about the compromised machine like the computer name, user name, language used by the machine, product name, operating system, network group, OS version, and file extension it generates for the encrypted files. Below is the example of the information in json format.

Defense Evasion
It will also execute a base 64 encoded PowerShell script command that will delete the shadow copy of the compromised machine.
Base 64 encoded:
powershell -e RwBlAHQALQBXAG0AaQBPAGIAagBlAGMAdAAgAFcAaQBuADMAMgBfAFMAaABhAGQAbwB3AGMAbwBwAHkAIAB8ACAARgBvAHIARQBhAGMAaAAtAE8AYgBqAGUAYwB0ACAAewAkAF8ALgBEAGUAbABlAHQAZQAoACkAOwB9AA==
Base 64 decoded:
Get-WmiObject Win32_Shadowcopy | ForEach-Object {$_.Delete();}
Detect REvil Ransomware with Splunk
REvil Registry Entry (New)
| tstats `security_content_summariesonly` count values(Registry.registry_key_name)
as registry_key_name values(Registry.registry_path) as registry_path min(_time)
as firstTime max(_time) as lastTime FROM datamodel=Endpoint.Registry where (Registry.registry_path="*\\SOFTWARE\\WOW6432Node\\Facebook_Assistant\\*" OR Registry.registry_path="*\\SOFTWARE\\WOW6432Node\\BlackLivesMatter*")
AND (Registry.registry_value_name = "\.*" OR Registry.registry_value_name = "Binary
Data") by Registry.registry_value_name Registry.dest Registry.user
| `security_content_ctime(lastTime)`
| `security_content_ctime(firstTime)`
| `drop_dm_object_name(Registry)`

REvil Common Exec Parameter (New)
| tstats count min(_time) as firstTime max(_time) as lastTime from datamodel=Endpoint.Processes
where Processes.process = "*-nolan*" OR Processes.process = "*-nolocal*" OR Processes.process = "*-fast*" OR Processes.process = "*-full*"
by Processes.process_name Processes.process Processes.parent_process_name Processes.parent_process Processes.dest Processes.user Processes.process_id Processes.process_guid

Modification Of Wallpaper (New)
sourcetype=XmlWinEventLog:Microsoft-Windows-Sysmon/Operational OR
source=XmlWinEventLog:Microsoft-Windows-Sysmon/Operational
EventCode =13 (TargetObject= "*\\Control Panel\\Desktop\\Wallpaper" AND Image != "*\\explorer.exe")
OR (TargetObject= "*\\Control Panel\\Desktop\\Wallpaper" AND Details = "*\\temp\\*")
| stats count min(_time) as firstTime max(_time) as lastTime by EventCode Image TargetObject Details Computer process_guid process_id user_id

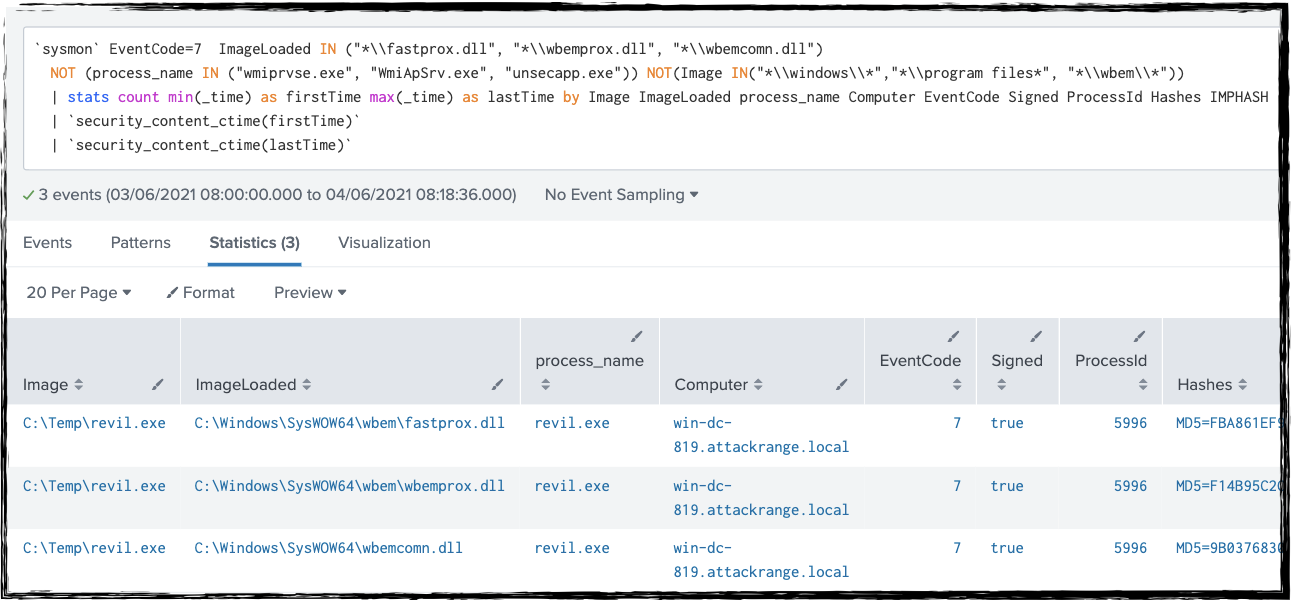
Wbemprox COM Object Execution (New)
sourcetype=XmlWinEventLog:Microsoft-Windows-Sysmon/Operational OR
source=XmlWinEventLog:Microsoft-Windows-Sysmon/Operational
EventCode=7 ImageLoaded IN ("*\\fastprox.dll", "*\\wbemprox.dll", "*\\wbemcomn.dll")
NOT (process_name IN ("wmiprvse.exe", "WmiApSrv.exe", "unsecapp.exe")) NOT(Image IN("*\\windows\\*","*\\program files*", "*\\wbem\\*"))
| stats count min(_time) as firstTime max(_time) as lastTime by Image ImageLoaded process_name Computer EventCode Signed ProcessId Hashes IMPHASH
Known Services Killed by Ransomware (New)
Sourcetype=WinEventLog:System EventCode=7036 Message IN
("*VSS*", "*backup*", "*sophos*", "*sql*", "*memtas*", "*mepocs*", "*veeam*", "*svc$*")
Message="*service entered the stopped state*"
| stats count min(_time) as firstTime max(_time) as lastTime by EventCode Message dest Type

Allow network Discovery In Firewall (New)
| tstats `security_content_summariesonly` count min(_time) as firstTime max(_time)
as lastTime from datamodel=Endpoint.Processes where Processes.process_name=netsh.exe
Processes.process= "*firewall*" Processes.process= "*group=\"Network Discovery\"*" Processes.process="*enable*" Processes.process="*Yes*"
by Processes.dest Processes.user Processes.parent_process Processes.process_name
Processes.process Processes.process_id Processes.parent_process_id Processes.parent_process_name
| `drop_dm_object_name(Processes)` | `security_content_ctime(firstTime)` | `security_content_ctime(lastTime)`

Disable Windows Behavior Monitoring (Updated)
| tstats `security_content_summariesonly` count min(_time) as firstTime max(_time)
as lastTime from datamodel=Endpoint.Registry where
Registry.registry_path= "*\\SOFTWARE\\Policies\\Microsoft\\Windows Defender\\Real-Time Protection\\DisableBehaviorMonitoring" OR
Registry.registry_path= "*\\SOFTWARE\\Policies\\Microsoft\\Windows Defender\\Real-Time Protection\\DisableOnAccessProtection" OR
Registry.registry_path= "*\\SOFTWARE\\Policies\\Microsoft\\Windows Defender\\Real-Time Protection\\DisableScanOnRealtimeEnable" OR
Registry.registry_path= "*\\SOFTWARE\\Microsoft\\Windows Defender\\Real-Time Protection\\DisableRealtimeMonitoring" OR
Registry.registry_path= "*\\Real-Time Protection\\DisableIntrusionPreventionSystem" OR
Registry.registry_path= "*\\Real-Time Protection\\DisableIOAVProtection" OR
Registry.registry_path= "*\\Real-Time Protection\\DisableScriptScanning"
Registry.registry_value_name = "DWORD (0x00000001)"
by Registry.registry_path Registry.registry_key_name Registry.registry_value_name
Registry.dest
| `drop_dm_object_name(Registry)`
| `security_content_ctime(firstTime)`
|`security_content_ctime(lastTime)`

| tstats `security_content_summariesonly` count min(_time) as firstTime max(_time)
as lastTime from datamodel=Endpoint.Processes where Processes.process_name IN ("powershell.exe", "pwsh.exe", "sqlps.exe", "sqltoolsps.exe")
Processes.process="*set-mppreference*" AND
Processes.process IN ("*disablerealtimemonitoring*","*disableioavprotection*","*disableintrusionpreventionsystem*","*disablescriptscanning*","*disableblockatfirstseen*")
by Processes.dest Processes.user Processes.parent_process Processes.process_name Processes.process Processes.process_id Processes.parent_process_id
| `drop_dm_object_name(Processes)`
| `security_content_ctime(firstTime)`
| `security_content_ctime(lastTime)`

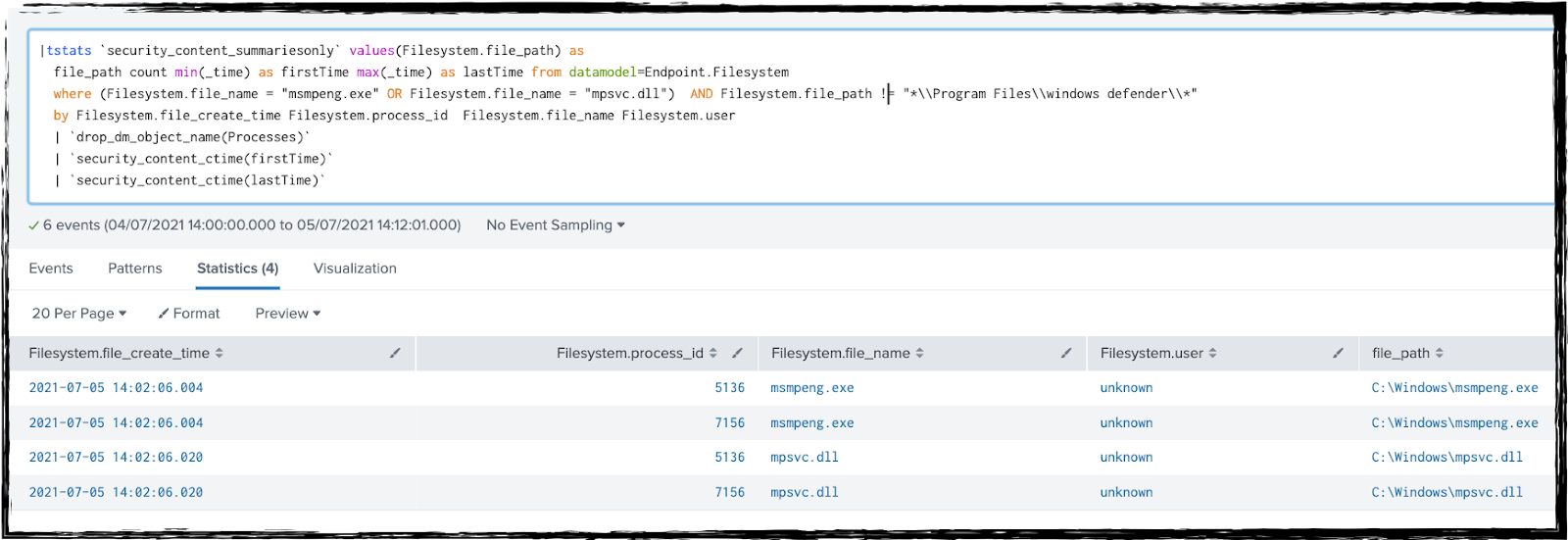
Msmpeng Application DLL Side (New)
| tstats `security_content_summariesonly` values(Filesystem.file_path) as
file_path count min(_time) as firstTime max(_time) as lastTime from datamodel=Endpoint.Filesystem
where (Filesystem.file_name = "msmpeng.exe" OR Filesystem.file_name = "mpsvc.dll") AND Filesystem.file_path != "*\\Program Files\\windows defender\\*"
by Filesystem.file_create_time Filesystem.process_id Filesystem.file_name Filesystem.user
| `drop_dm_object_name(Processes)`
| `security_content_ctime(firstTime)`
| `security_content_ctime(lastTime)`
Detection | Techniques ID | Tactics | Description |
Impact | Detects deletion of shadow copy with PowerShell | ||
Registry Keys Used For Persistence (Existing) | Persistence, Privilege Escalation | Detects registry entry for persistence or privilege escalation | |
Ransomware Notes bulk creation (Existing) | Impact | Detects suspicious bulk creation of ransomware notes (.txt, hta, html) in compromised machine | |
High Process Termination Frequency(Existing) | Impact | Detects a suspicious big number of terminated processes within a time frame. | |
Suspicious Process File Path (Existing) | Persistence, Privilege Escalation | Detects process with suspicious file path | |
Revil Registry Entry (New) | Defense Evasion | Detects registry entry of REvil ransomware | |
Execution | Detects common parameter of REvil ransomware | ||
Impact | Detects suspicious events that modify the wallpaper of a host. | ||
Defense Evasion | Detects a suspicious wbemprox COM OBJ execution | ||
Impact | Detects termination of Known Services killed by ransomware | ||
Allow Network Discovery In Firewall (New) | Defense Evasion | Allow or Enable network discovery in firewall rules | |
Disable Windows Behavior Monitoring (Updated) | Defense Evasion | Disabling Windows Defender Artifacts in Registry | |
Powershell Disable Security Monitoring (New) | Defense Evasion | Disabling Windows Defender Artifacts in Registry | |
Msmpeng Application DLL Side Loading | Hijack Execution Flow: dll Side loading | Execute dll side loading of msmpeng.exe application |
Hashes
REvil Ransomware:
SHA256: 33026ba868a6159223b486b57caebe40926208bb80b89749318e51dcd5b8b883
Mitigation
For mitigation of this and similar ransomware threats please use CISA guidance for reference: https://www.cisa.gov/ransomware
We hope that this information is helpful. Our team is standing by to help if you need it.
Related Articles
About Splunk
The world’s leading organizations rely on Splunk, a Cisco company, to continuously strengthen digital resilience with our unified security and observability platform, powered by industry-leading AI.
Our customers trust Splunk’s award-winning security and observability solutions to secure and improve the reliability of their complex digital environments, at any scale.