Defending Against the Log4j Vulnerabilities
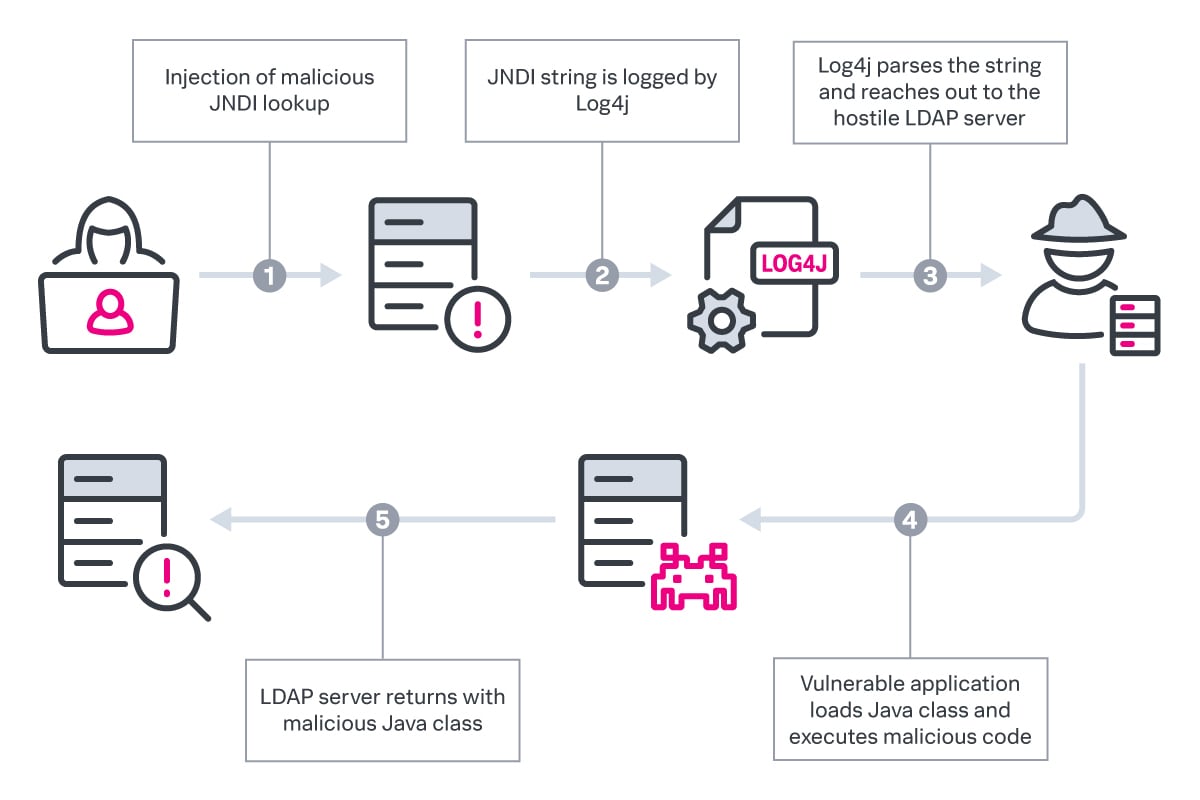
The Log4Shell vulnerability was first found in the popular Apache Log4j 2. It’s a critical zero-day vulnerability that enables bad actors to perform remote code execution (RCE). Log4j is used in frameworks, such as Apache Struts 2, Apache Solr, Apache Druid and Apache Flink.
In many instances, system admins may not be aware that Log4j is being used in their environments, leaving thousands of applications and third-party services at risk. Additional Log4j vulnerabilities have continued to add complexity to response efforts for many organizations.
Review and update your log types ingested into Splunk, then look for evidence of Log4j activity using process execution logs or file creation logs.
Use GitHub data in Splunk to find Log4j in your projects.
Search for compromised hosts with Network Traffic and DNS query logs.
Install Splunk Security Essentials and check out Splunk Research for detections to investigate and respond.
Look for other signs of code execution from external hosts and sources.
Expand monitoring across your IT infrastructure.
Simulating, Detecting, and Responding to Log4j vulnerabilities
Watch this video to see how the Splunk Threat Research Team (STRT) replicated an attack chain using the Log4j vulnerability to compromise a host.
This proof-of-concept enabled the STRT to develop detections and responses to detect adversaries exploiting this vulnerability that you can start using today.
Using Splunk Intelligence Management to combat Emerging Threats
Watch this video to see how a real security team took advantage of the Splunk Intelligence Management solution to save time from the manual handling and curation of Indicators related to this emerging threat and to improve their investigation efforts.



